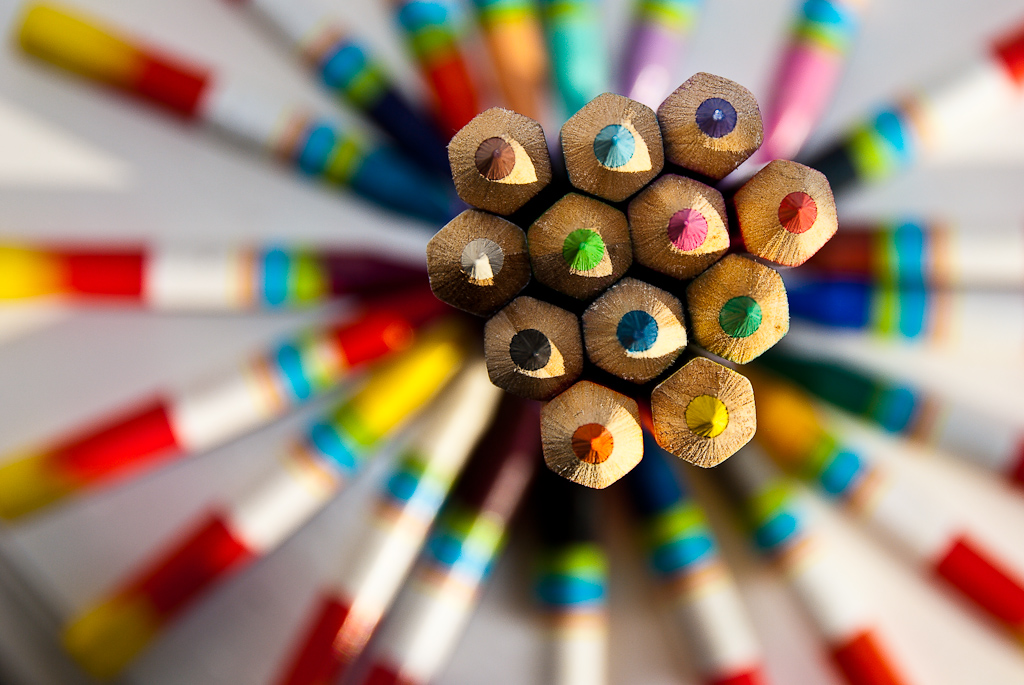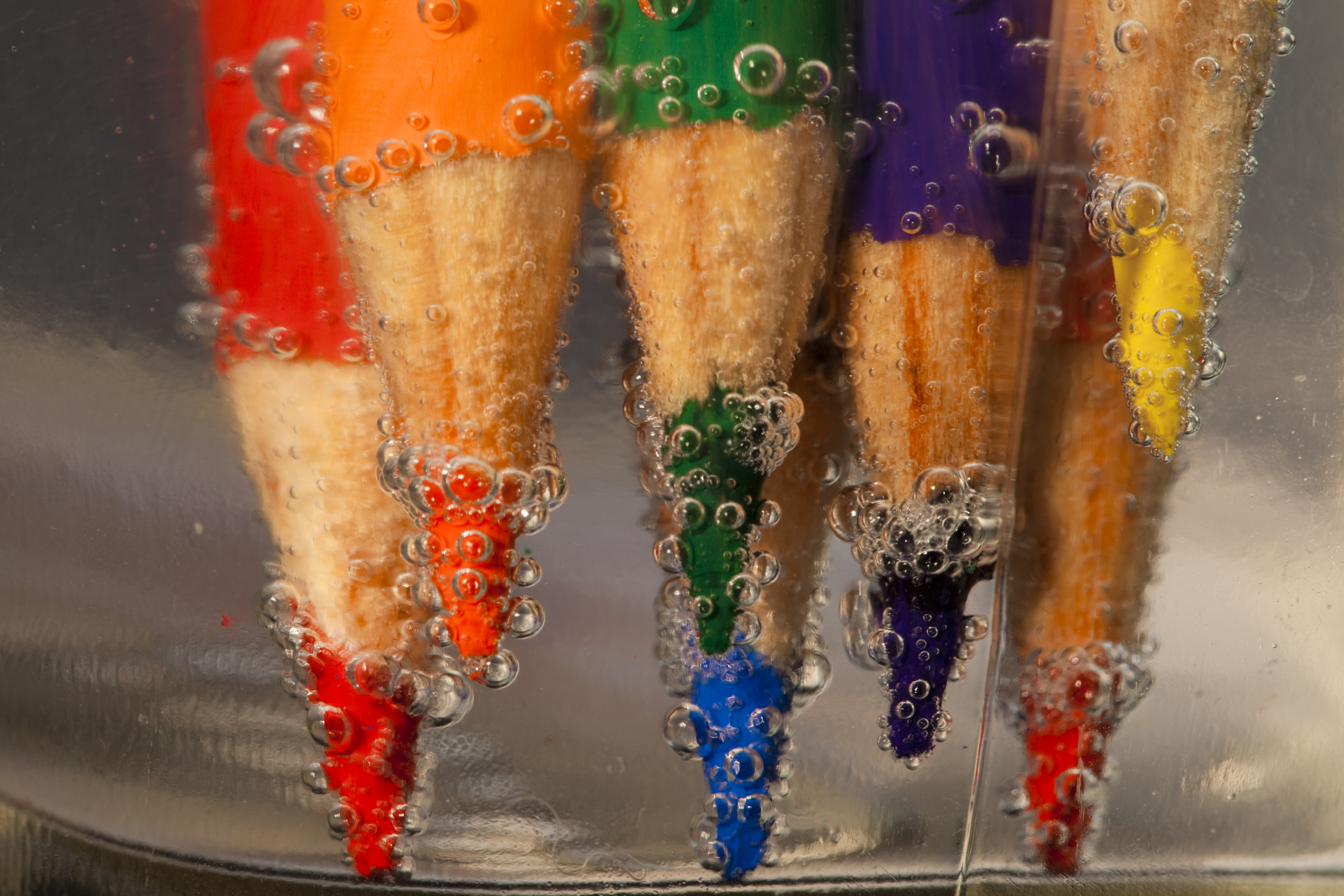“30 Fabulous Photos of Pencils” plus 4 more: Digital Photography School |
 |
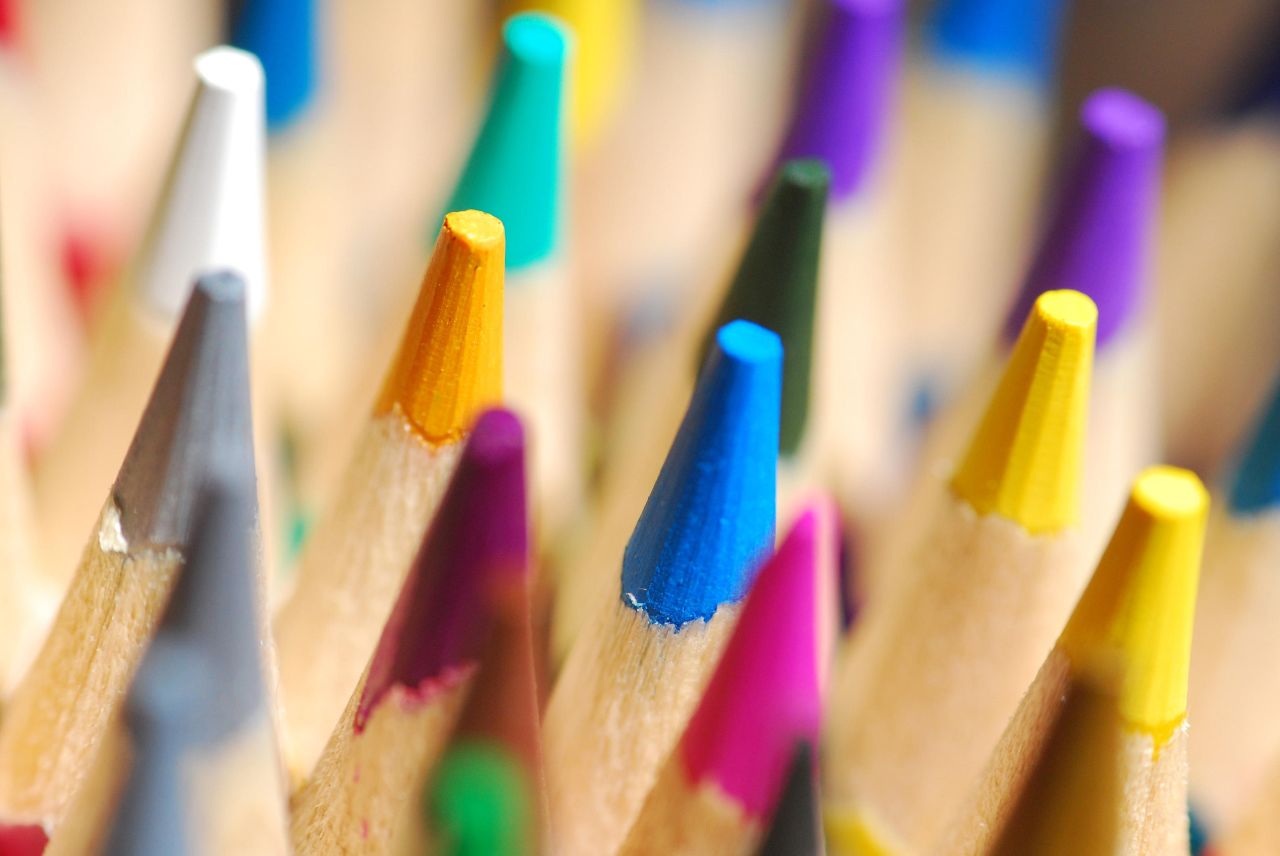
- 30 Fabulous Photos of Pencils
- Sending Panorama Sequences from Lightroom to Photoshop
- 5 HOT Posts From Our Archives You Would Have Seen if You Were Following us on Facebook
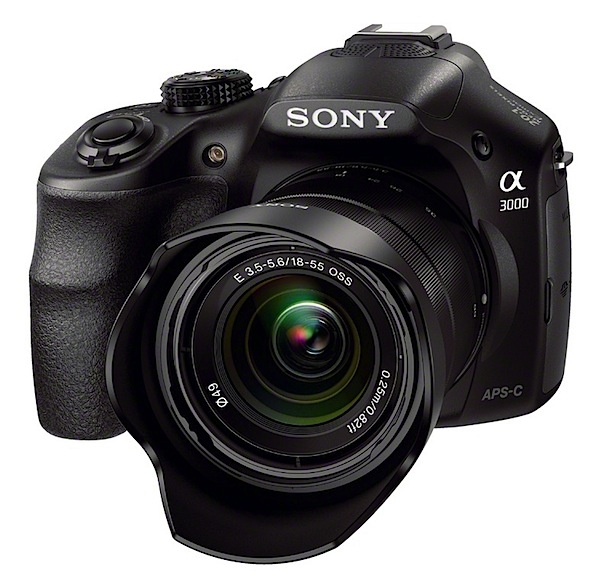
- Sony A3000 Review
- The Path to Better Photography
|
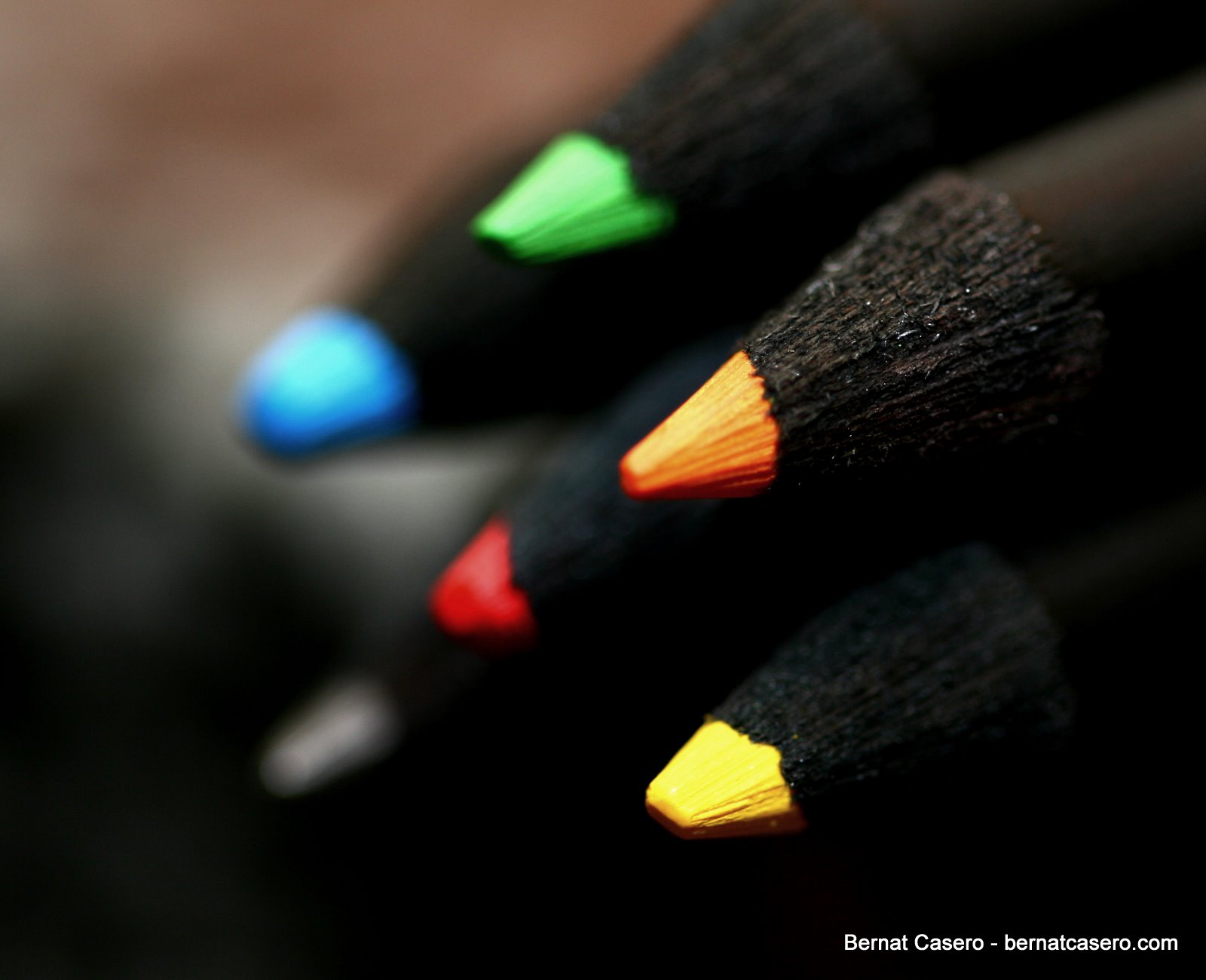
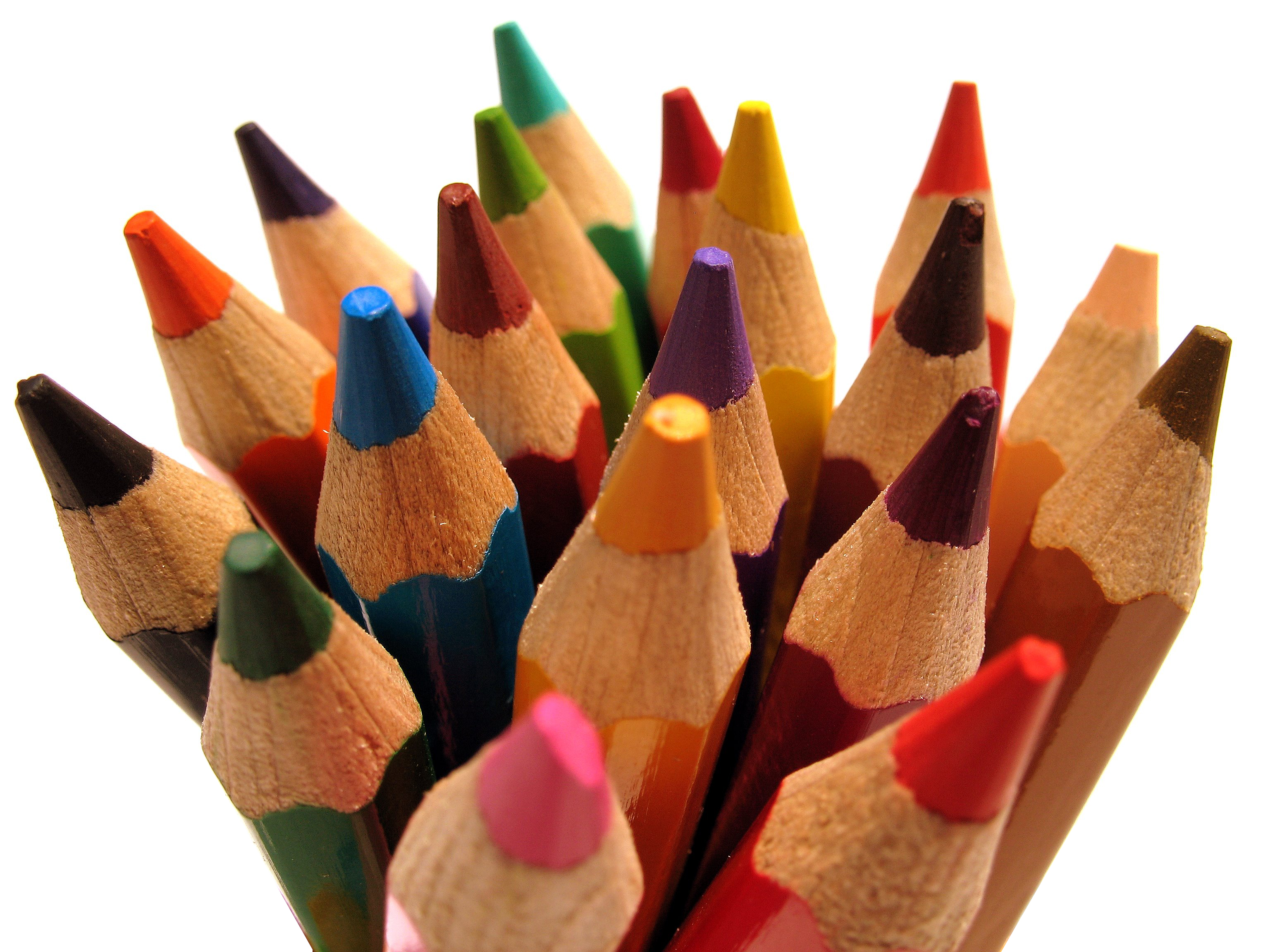
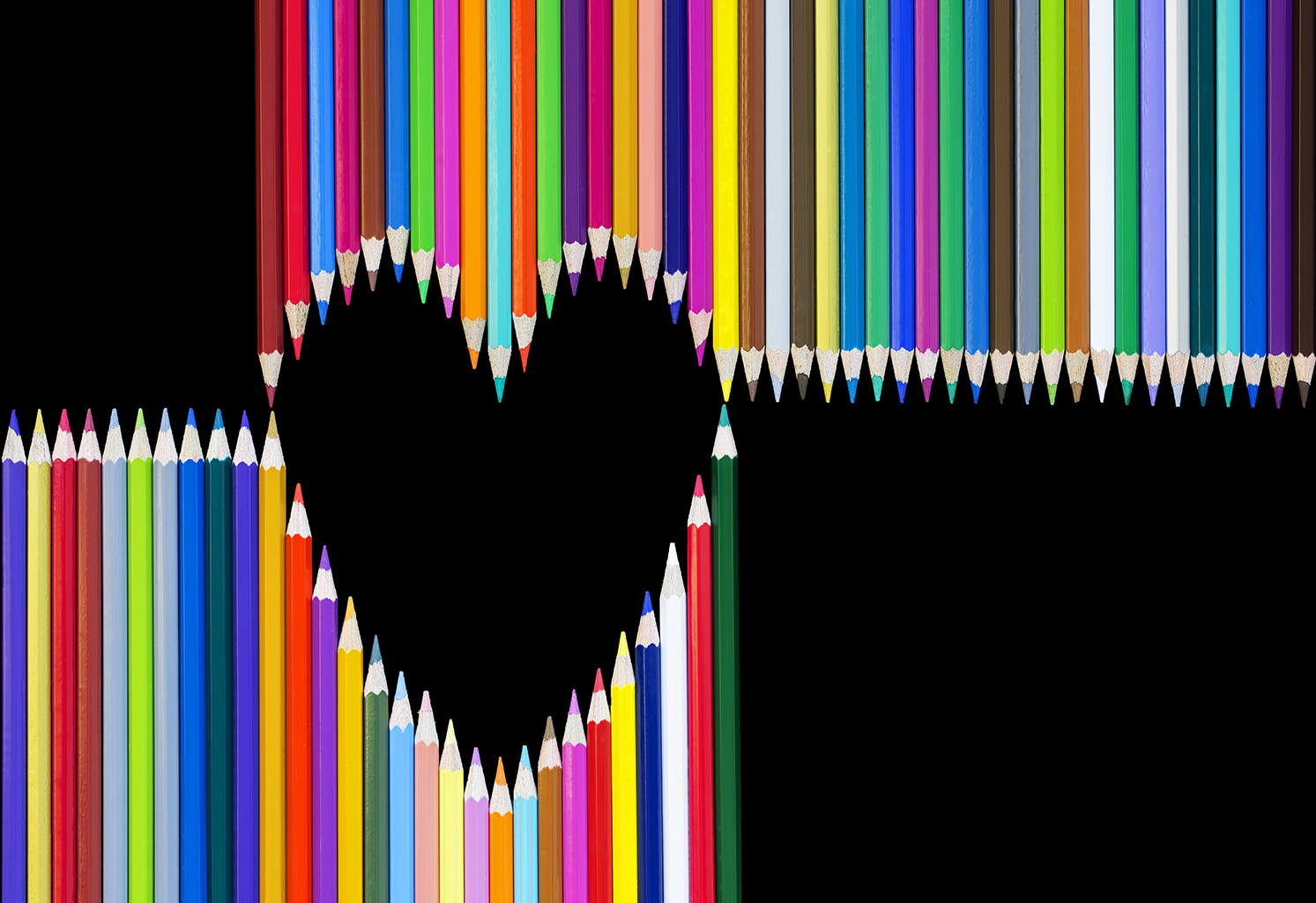
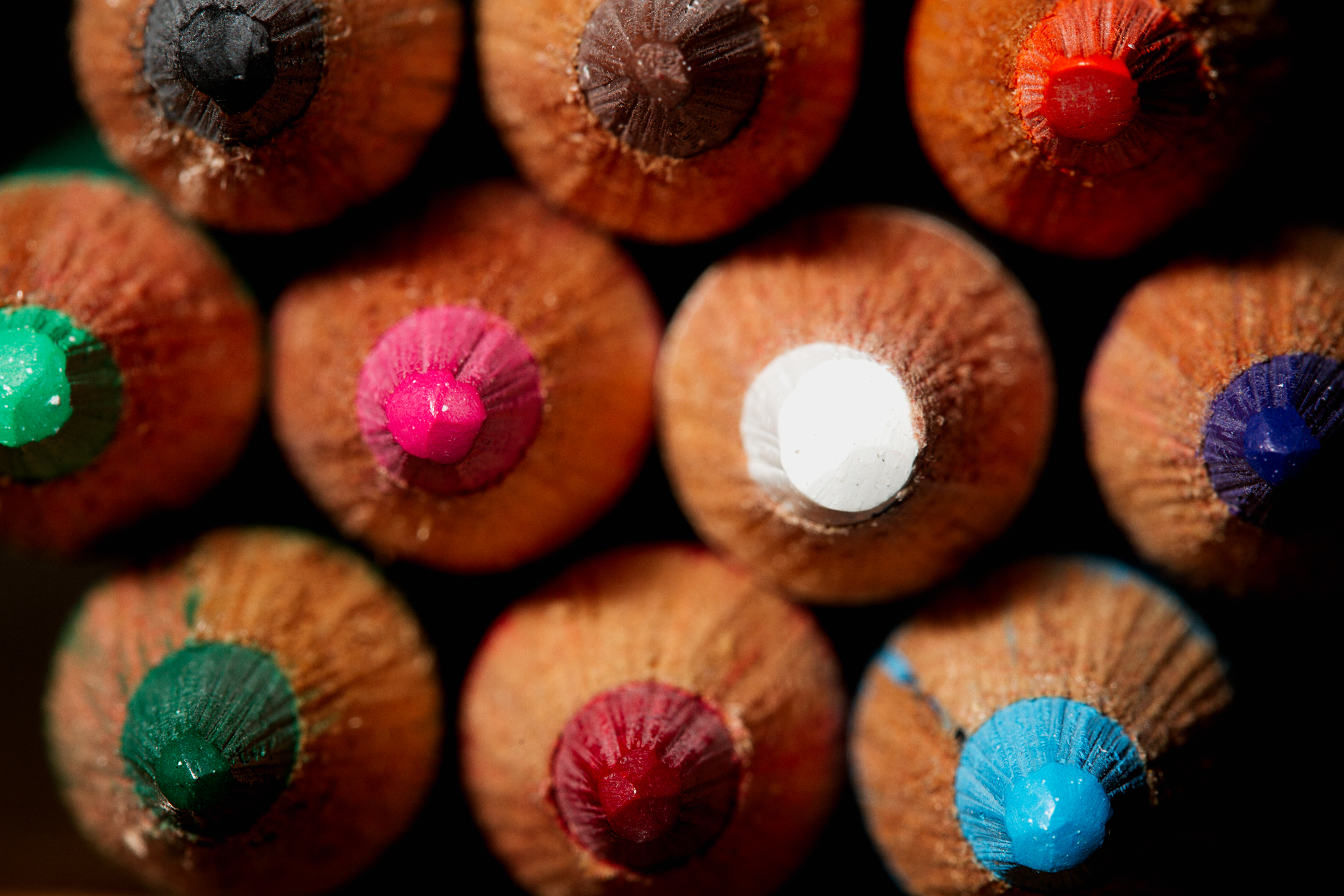
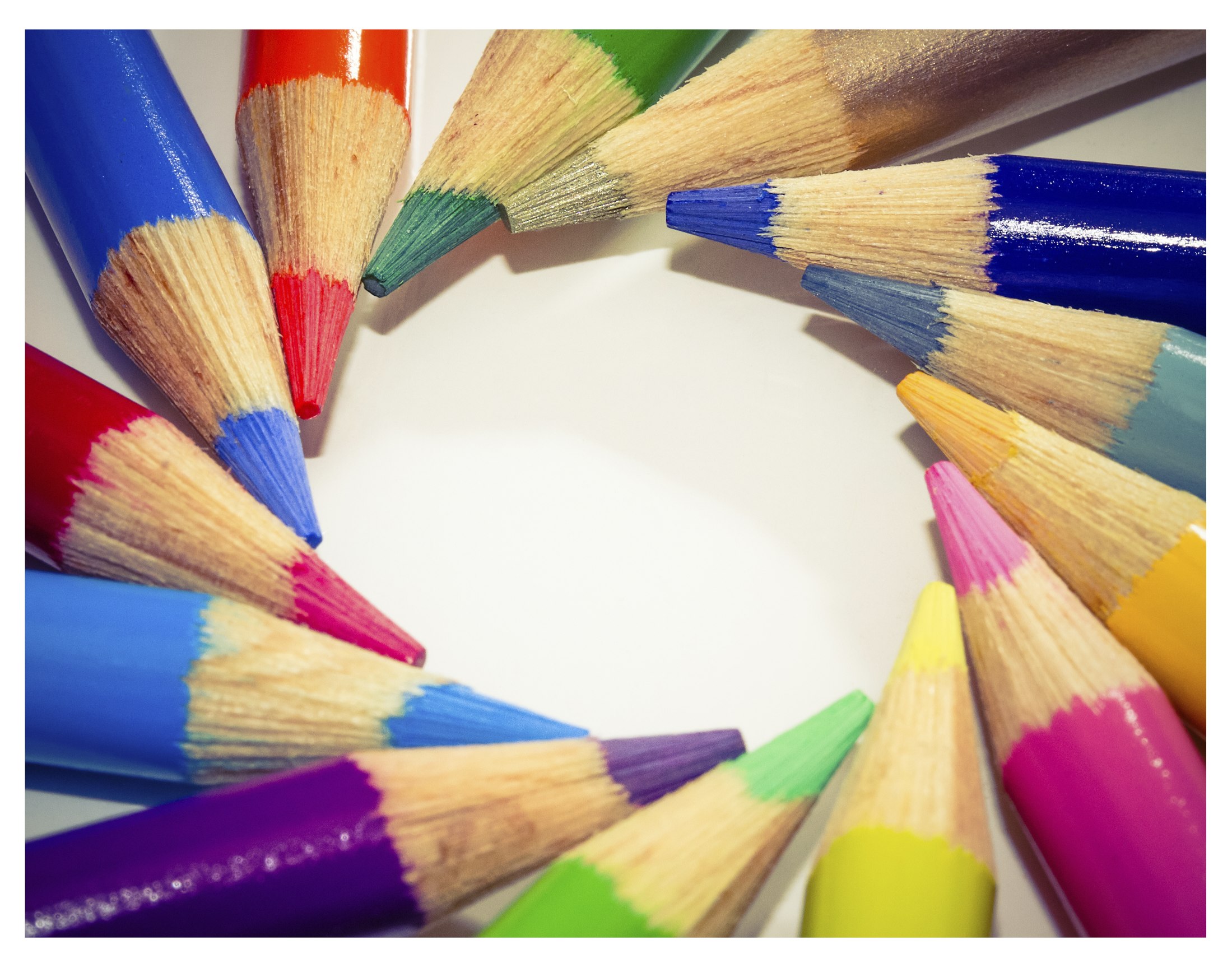
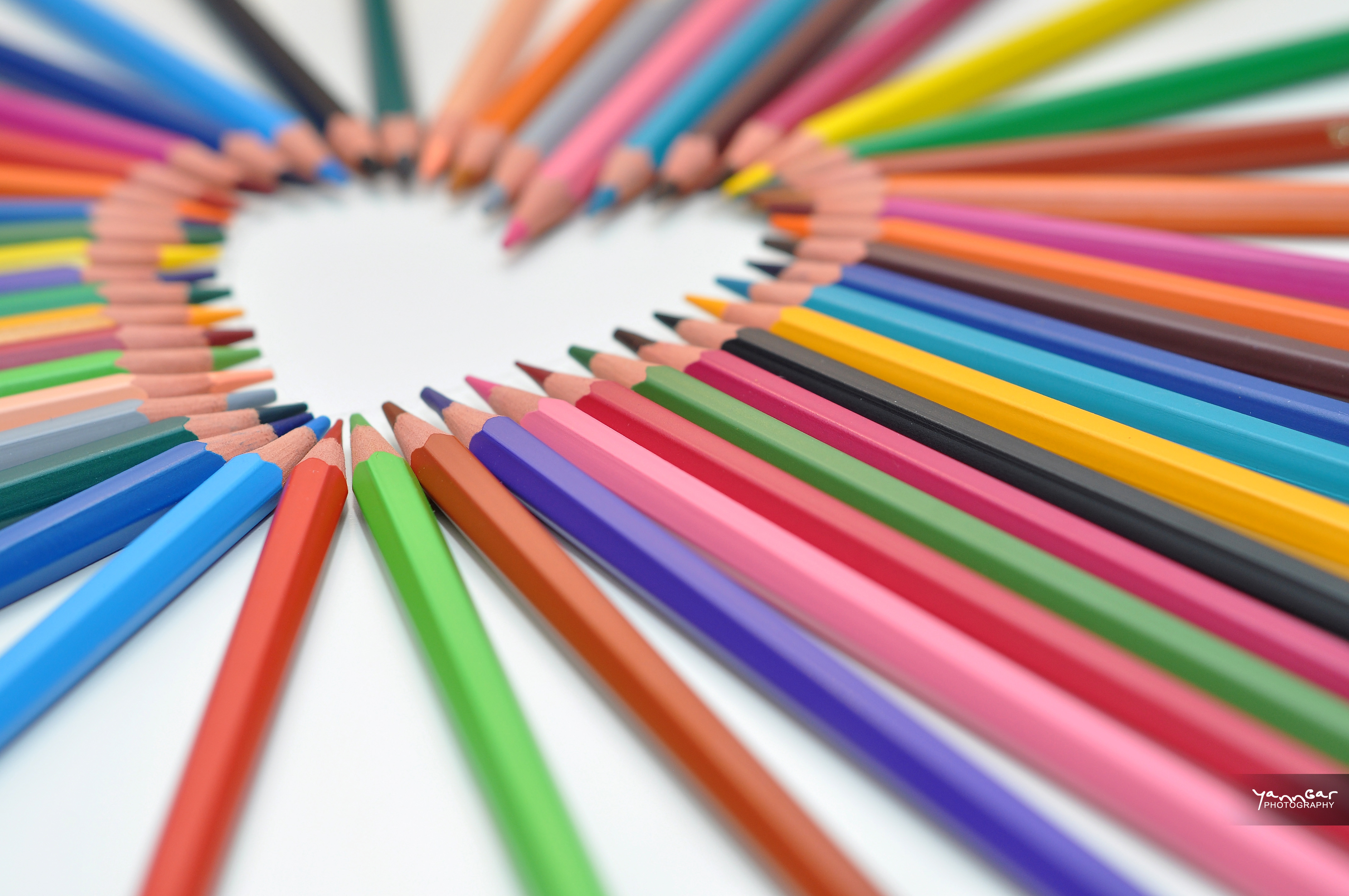
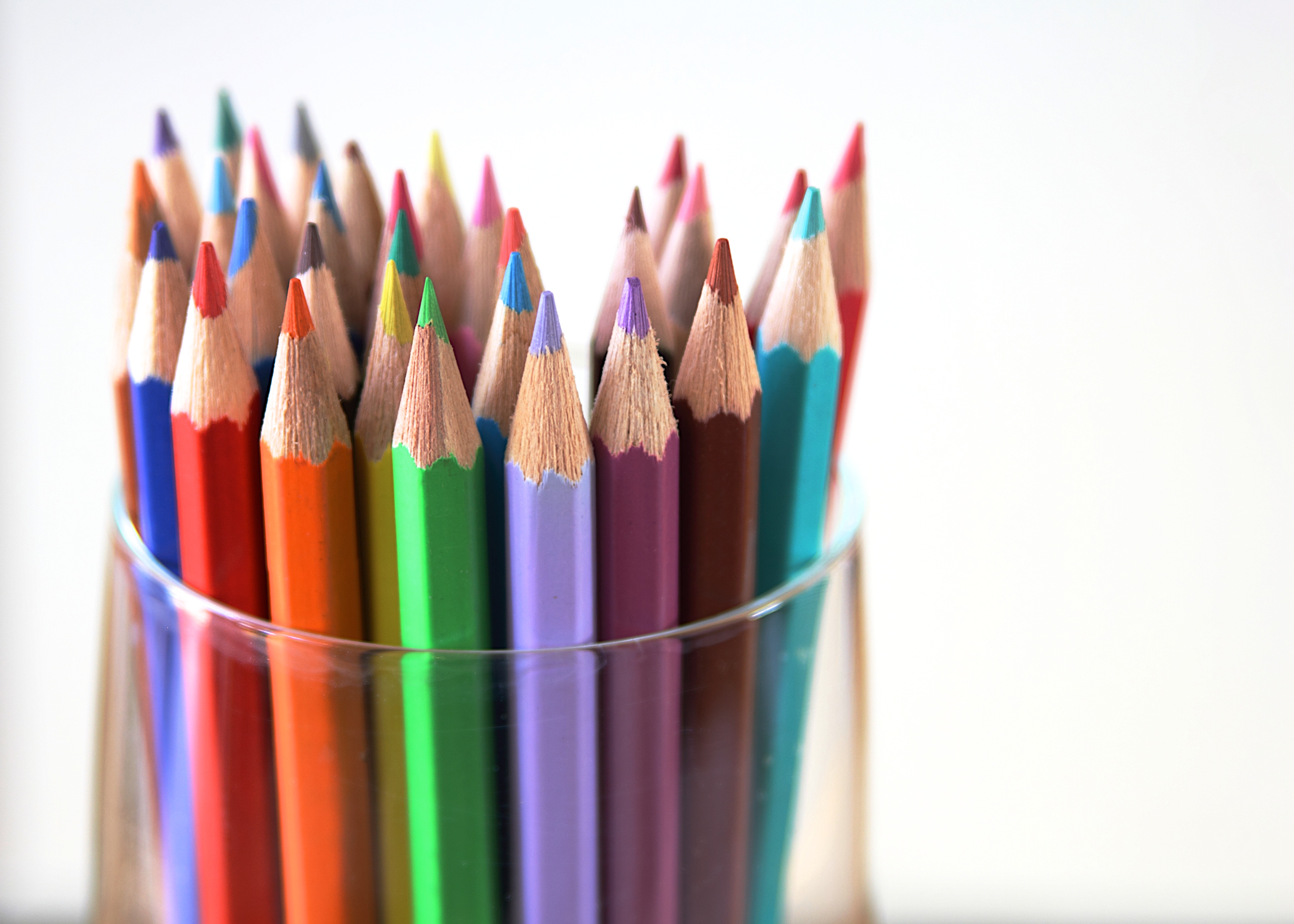
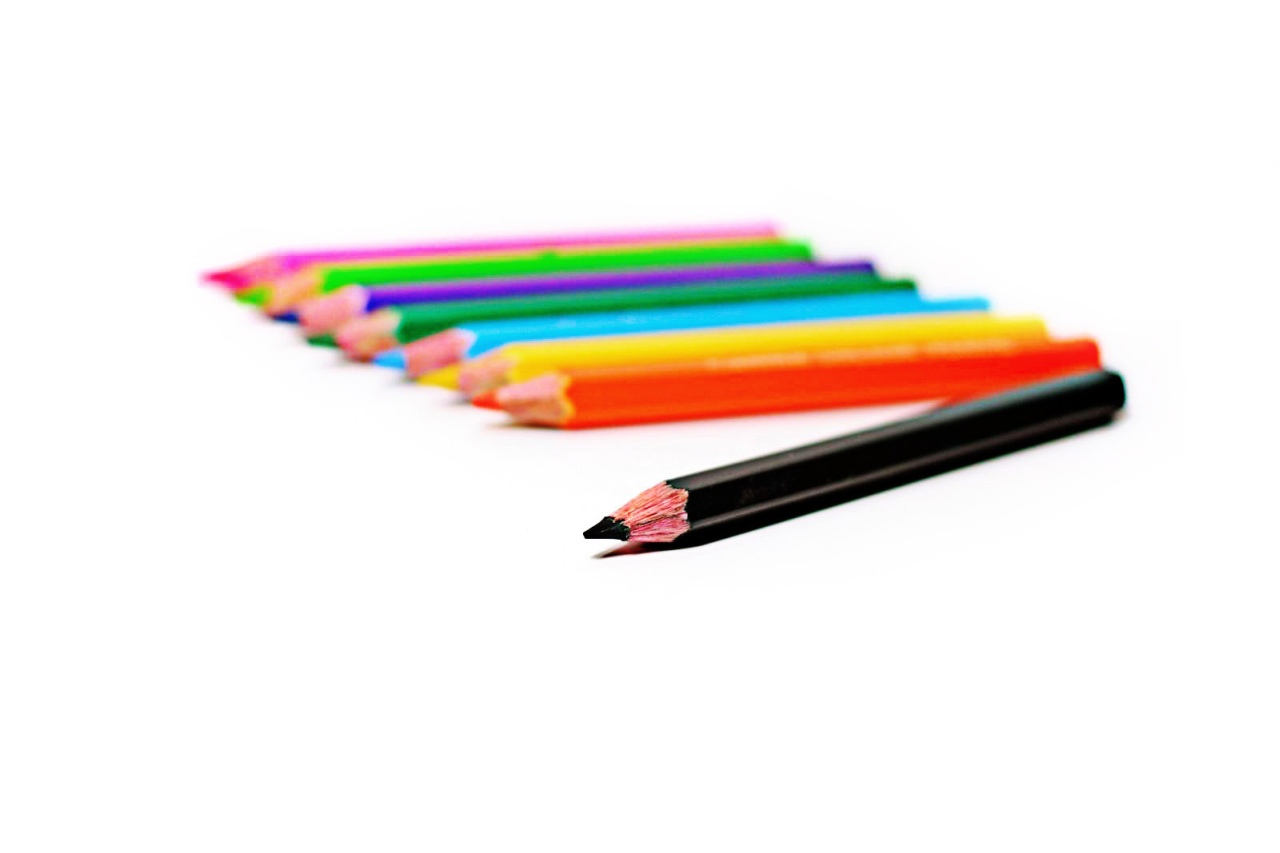
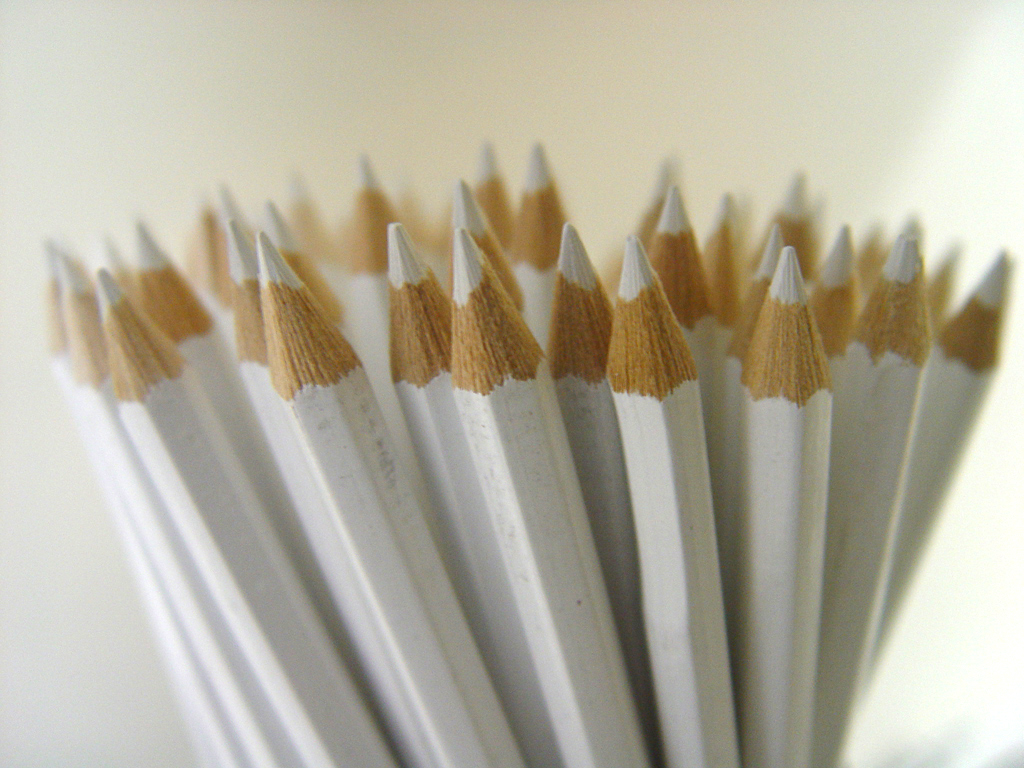
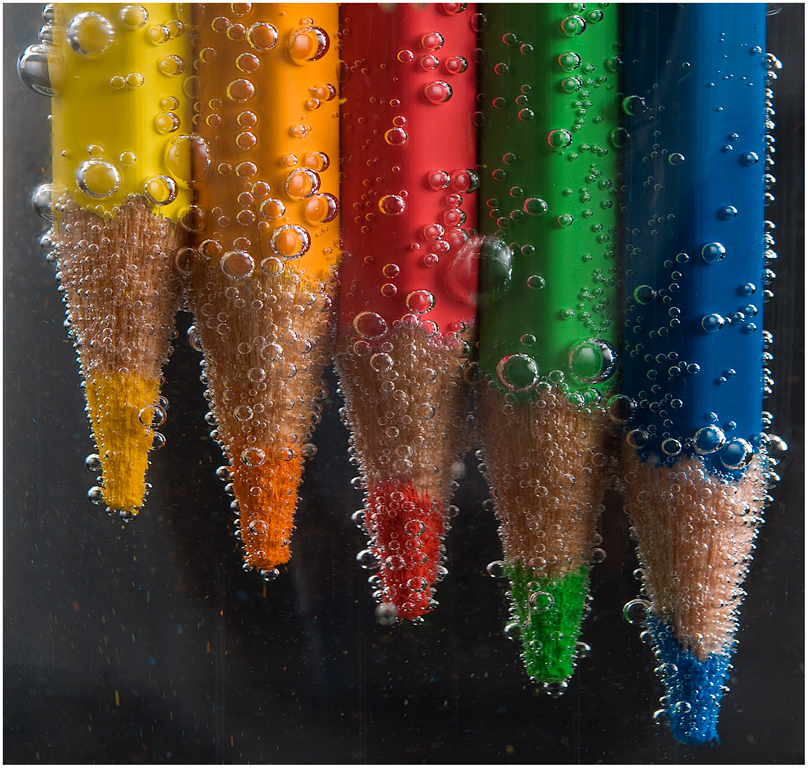
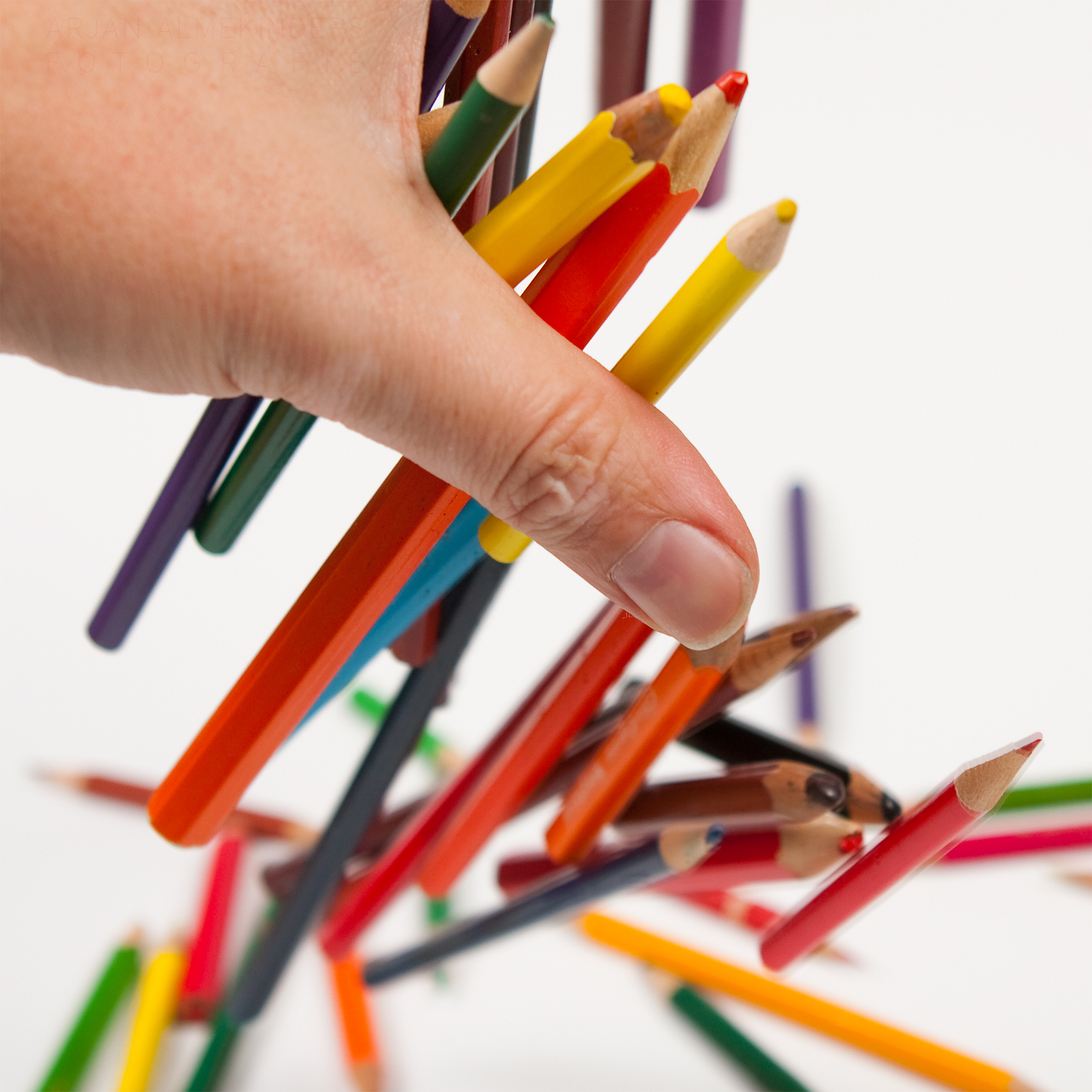
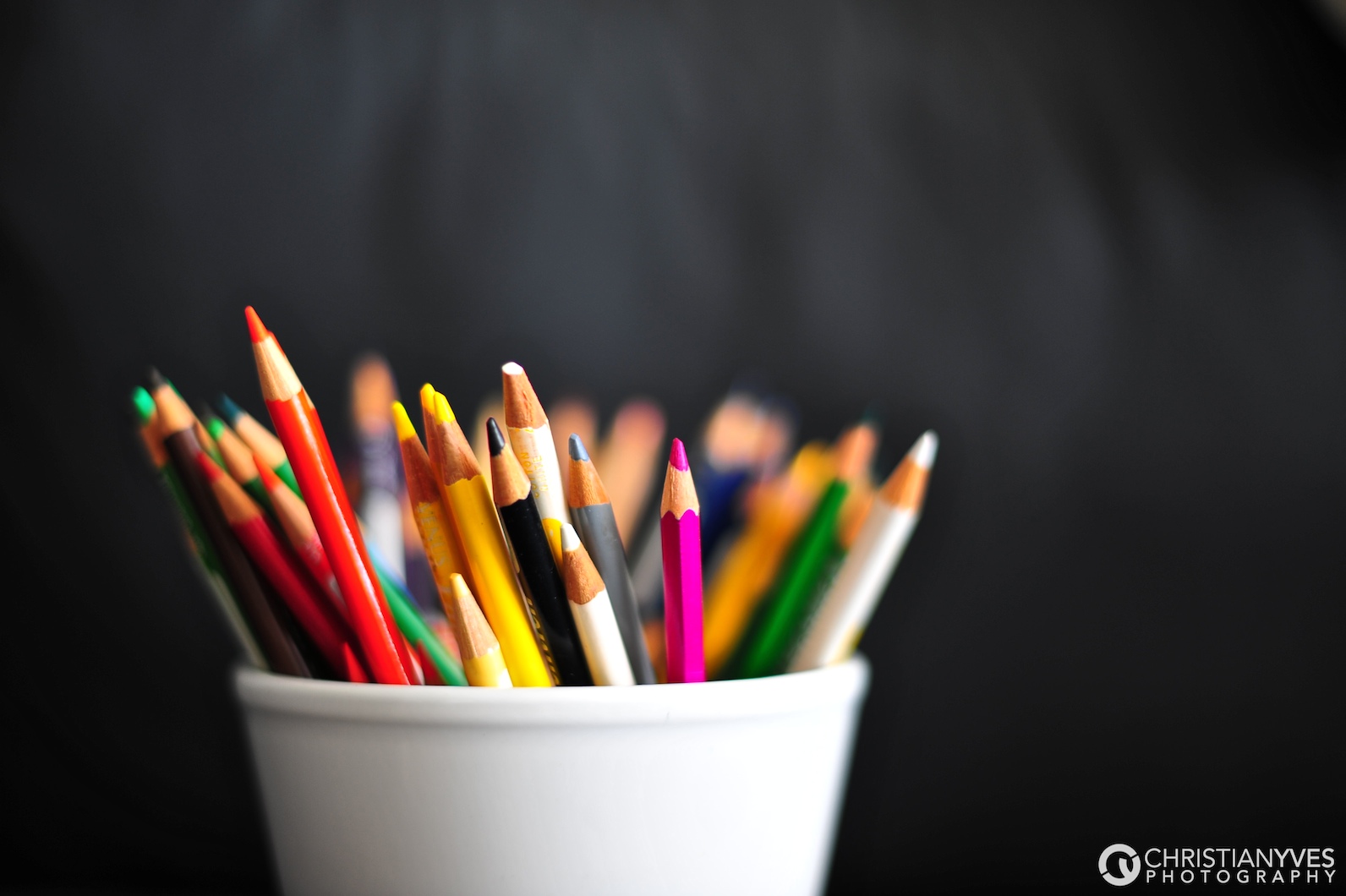
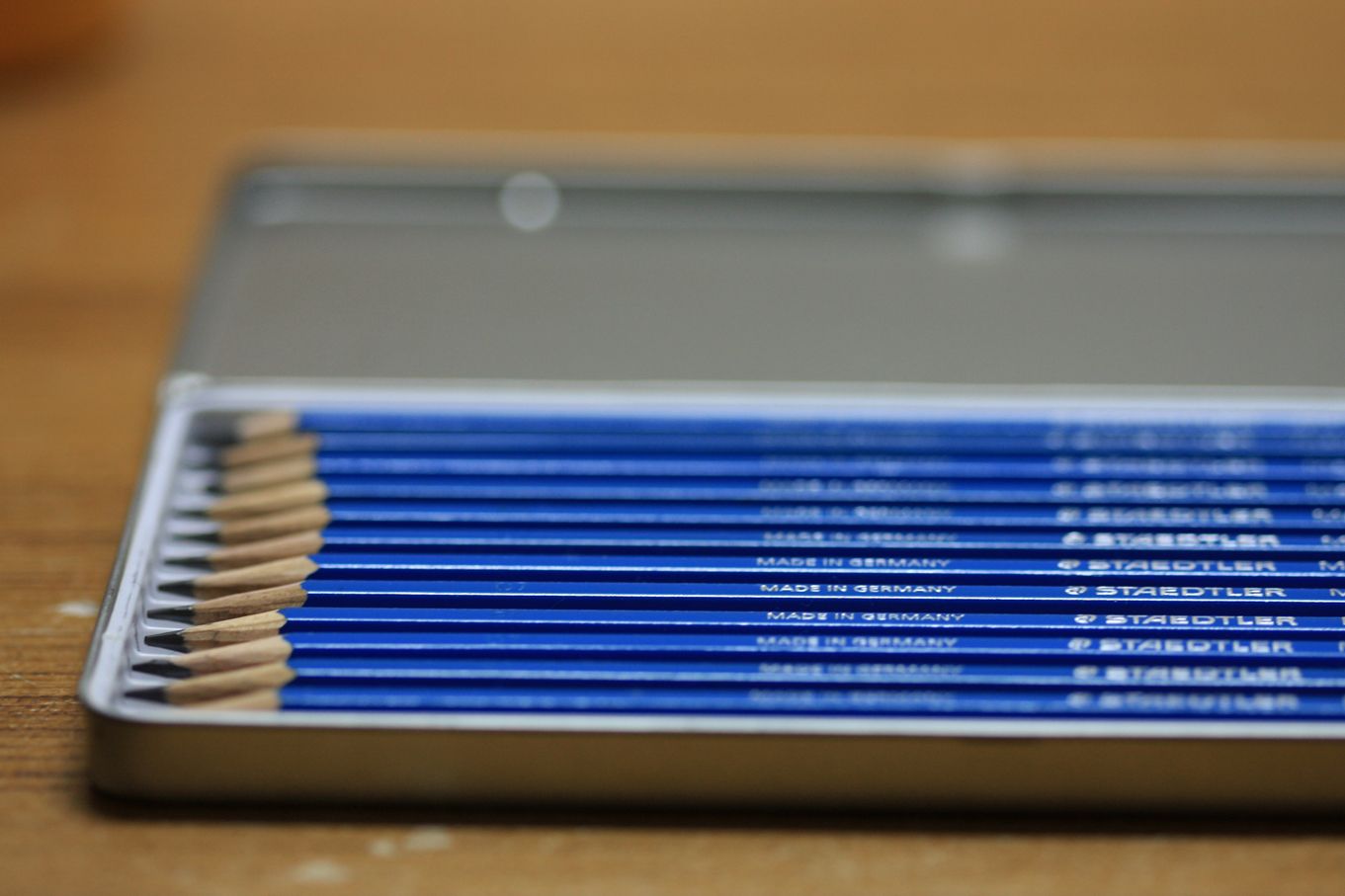
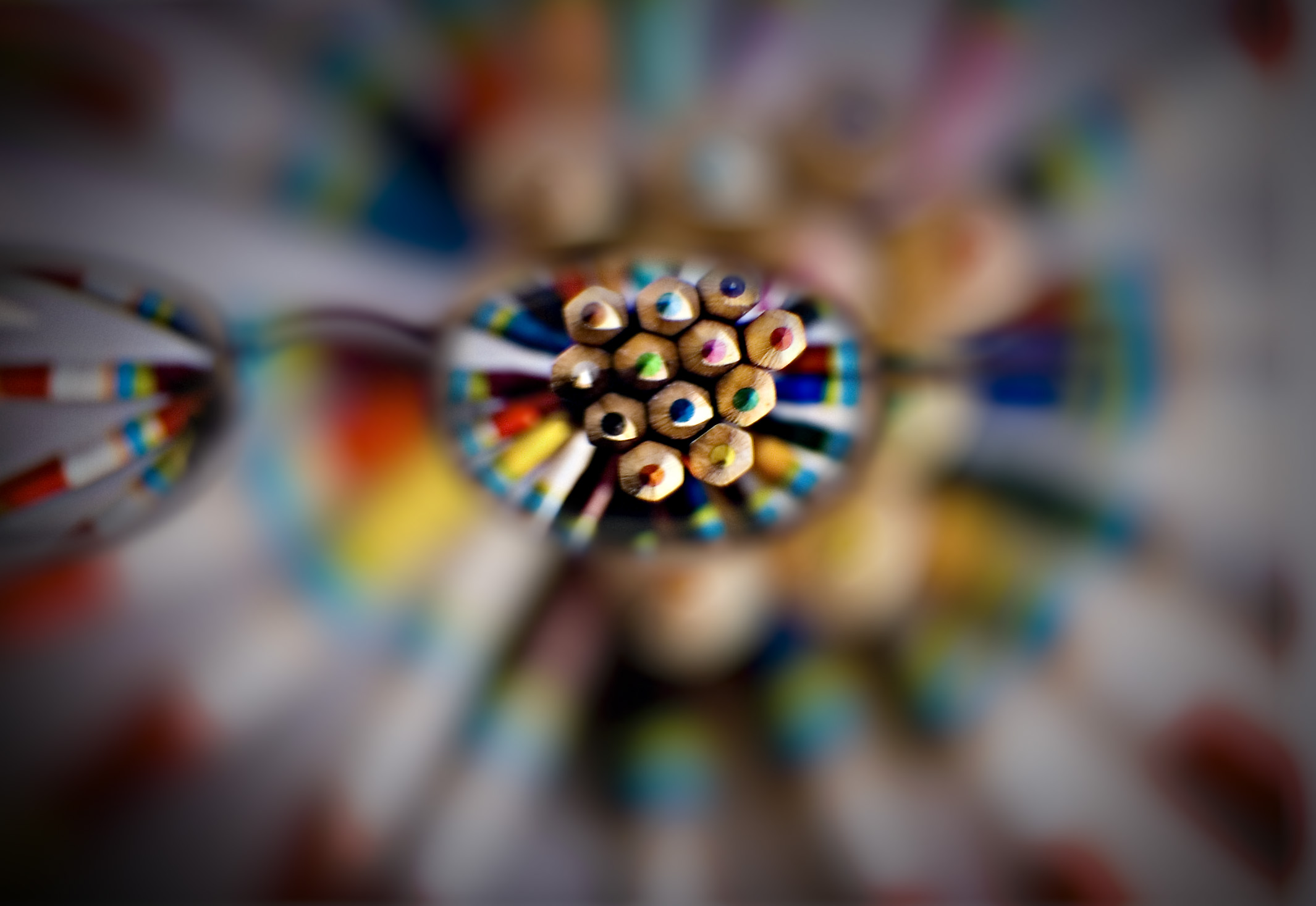
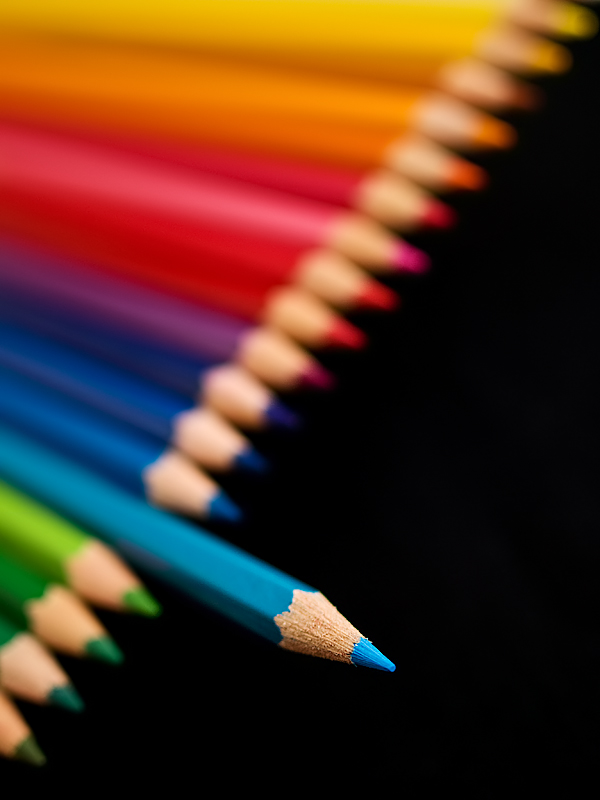
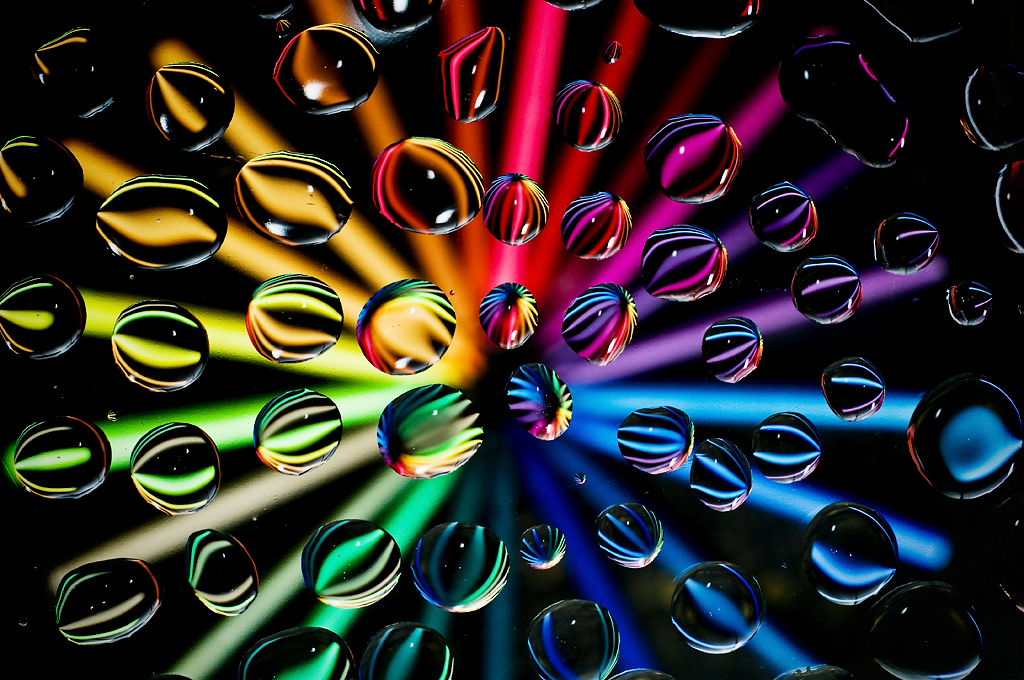
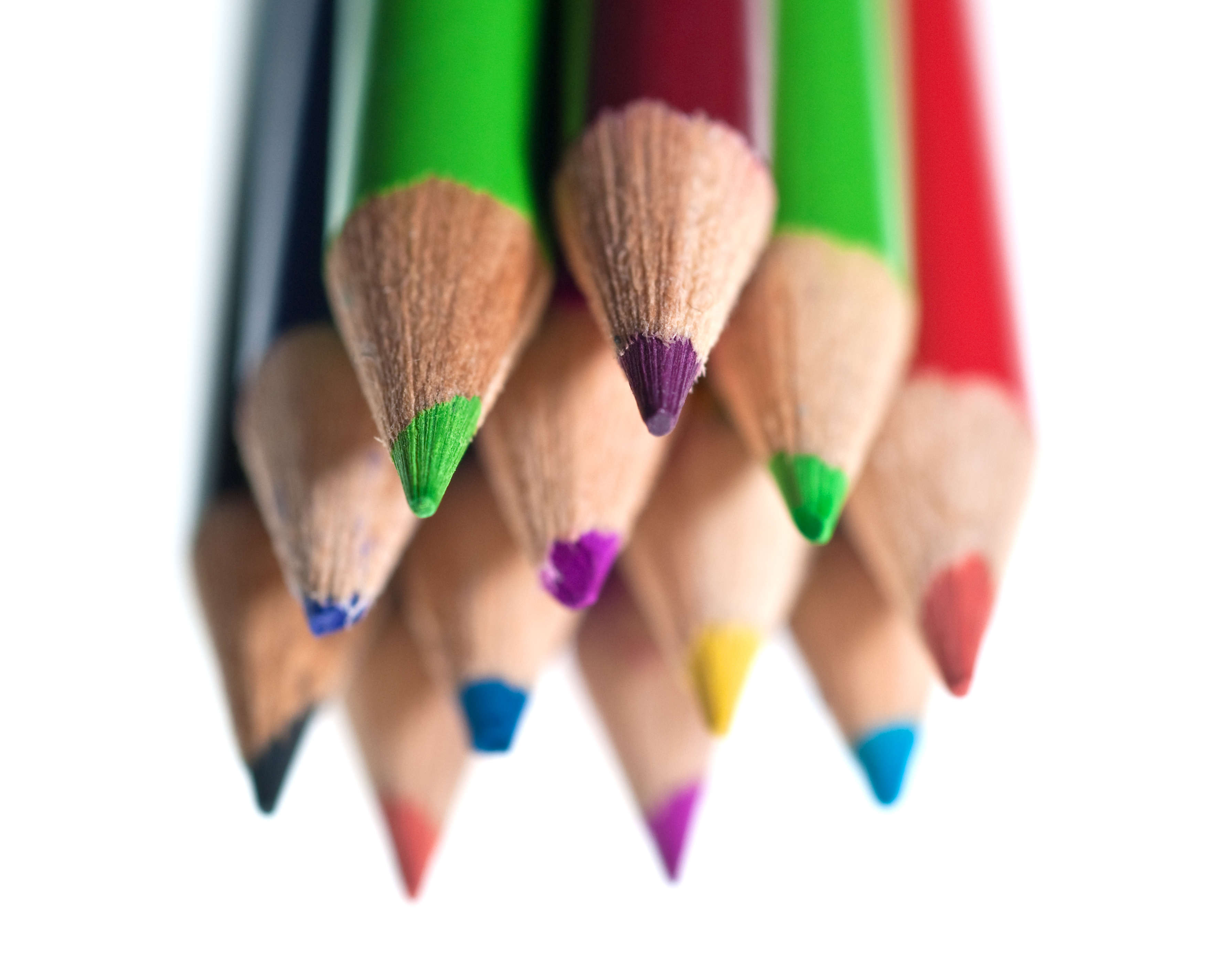
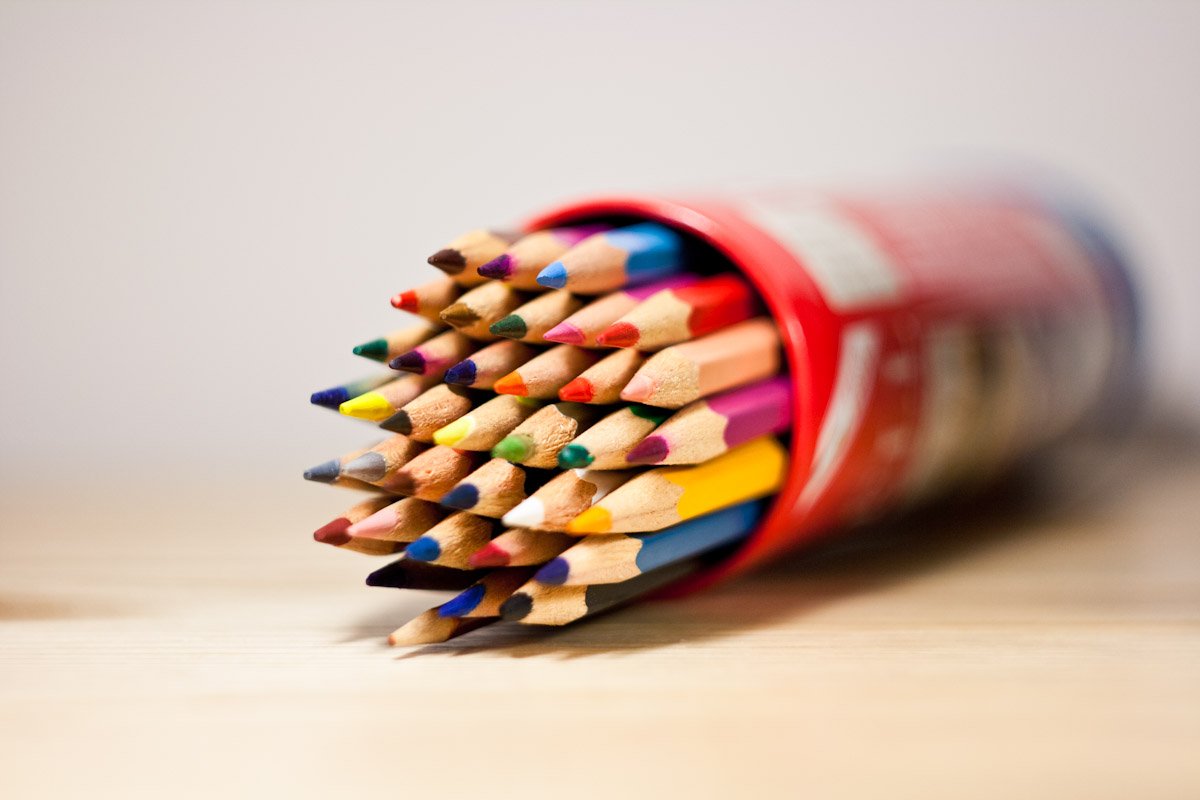
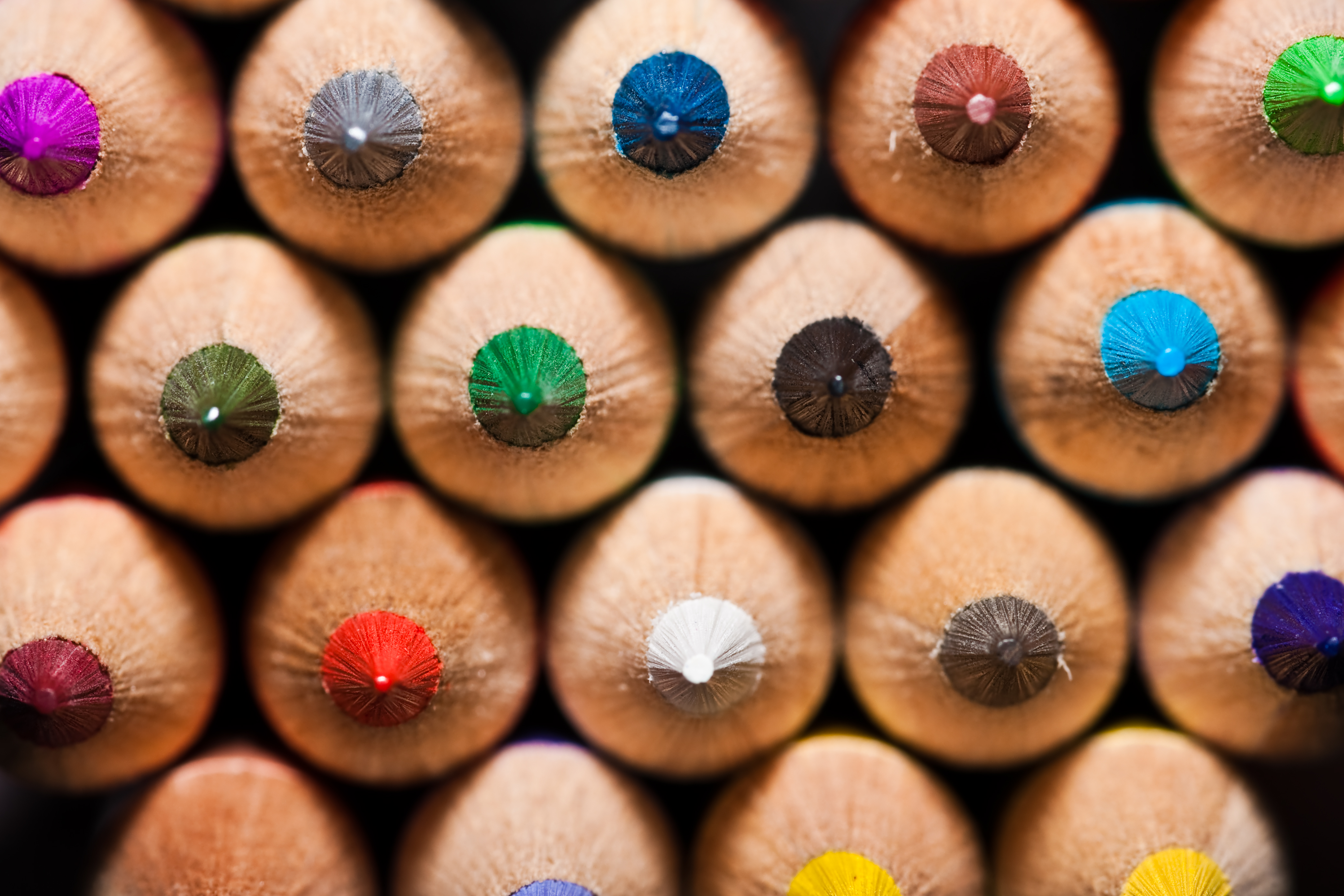
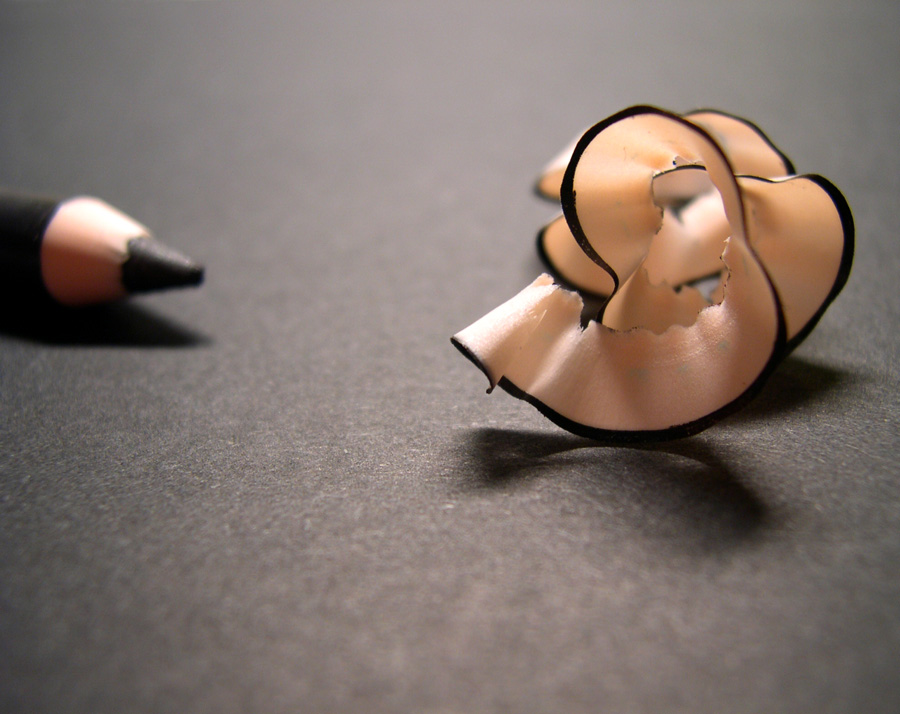
Posted: 07 Nov 2013 10:57 AM PST It is going to be a rainy weekend where I live and I’m looking for a photographic project to amuse myself with. One challenge I love setting myself on such weekends when I’m trapped inside is to take an everyday item and to photograph it. Take the humble Pencil. It is something that most households would have… particularly those of us with kids. We probably see them every day – so why not make it the focus of your attention for the weekend. Here’s how 30 other photographers have tackled the challenge of photographing pencils!
Post originally from: Digital Photography Tips. Check out our more Photography Tips at Photography Tips for Beginners, Portrait Photography Tips and Wedding Photography Tips. The post 30 Fabulous Photos of Pencils by Darren Rowse appeared first on Digital Photography School. |
|
Sending Panorama Sequences from Lightroom to Photoshop Posted: 07 Nov 2013 05:37 AM PST
In addition to being able to send single images from Lightroom to Photoshop for editing you can also send a series of images to Photoshop to assemble into a panorama. This is a useful because the Photoshop panorama merge feature is pretty good (certainly since the improvements in Photoshop CS3 & CS4) and other Photoshop tools such as Content Aware Fill and the Lens Correction Filter are handy for finishing your panoramas. When you are done, click Save and the completed panorama will be sent back to Lightroom for further processing. To see how this is done, begin inside Lightroom and select the images to assemble into a panorama. I like to put these into a collection so they are handy if I want to try multiple panorama options to select the best of them. I don’t typically process the images before sending them to Photoshop and, instead, I process the completed panorama when it returns to Lightroom. One exception to this is fixing the white balance if it were incorrectly set on the camera at capture time, for example. Photoshop can assemble panoramas both vertically and horizontally and it can also take a mix of images such as I used here. This sequence is six shots horizontally across the front of a building and one extra shot to handle the building’s tower which wasn’t captured in the original sequence. If I’d been thinking, I would have captured some extra sky to use but we can solve that in Photoshop.
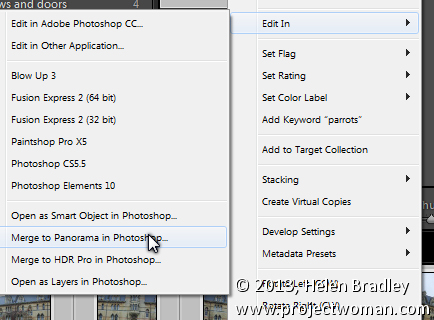
Select the images, right click and choose Edit In > Merge to Panorama in Photoshop.
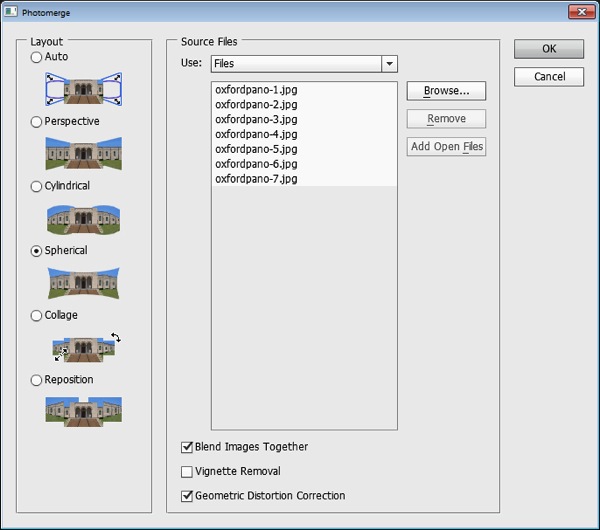
Photoshop will open with the images you sent to Photoshop listed in the Photomerge dialog. Now you need to determine the Layout to use. In most cases the Auto setting will be a good choice – when you select this, Photoshop will analyze the images and determine the best of the other layout alternatives: Perspective, Cylindrical and Spherical to use.
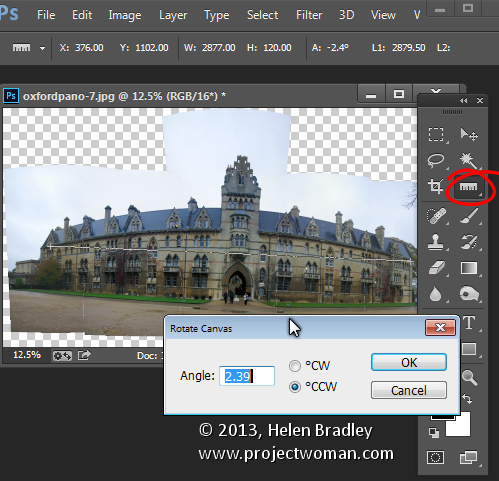
Check the Blend Images Together checkbox so that the images will be seamlessly blended together – then you won’t have to do it yourself. You can also click Geometric Distortion Correction to remove the effect of any barrel, pincushion or fisheye distortion in the original images. If the edges of your images have some edge vignetting click Vignette Removal. If you’re unsure what to choose, check all three checkboxes. Click Ok and wait as the images are aligned and blended. Once the panorama is assembled you can straighten the image if desired. To do this select all the layers and target the Ruler tool. Now drag along a line in the image which should be perfectly horizontal – you won’t be able to click the Straighten Layer button to rotate the image because you will have multiple layers selected. Instead, choose Image > Image Rotation > Arbitrary and click Ok to straighten the entire image to the angle of the Ruler line.
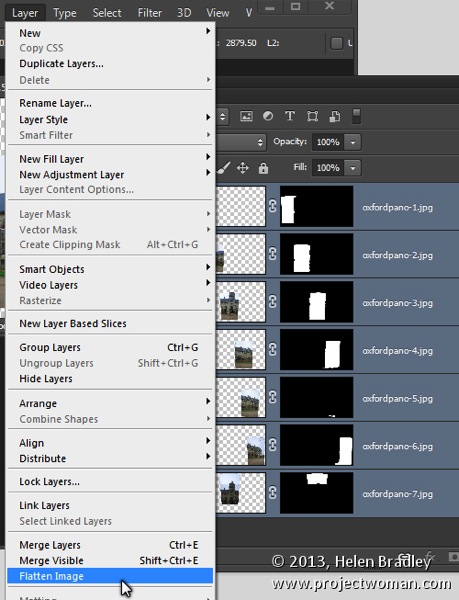
Most panoramas will then need to be cropped to a rectangle to eliminate uneven areas around the edge of the image. However, before you do this you may want to fill in some of the empty areas of the image using the Content Aware Fill tool so you can crop larger than you would otherwise be able to do. To do this you’ll either need to flatten the image to a single layer or you will need to create a new layer with the entire image on it to use. To flatten the image choose Layer > Flatten Image. To make a new layer with the image on it (but still retain the individual layers below) click the topmost layer and press Control + Alt + Shift + E (Command + Option + Shift + E on the Mac).
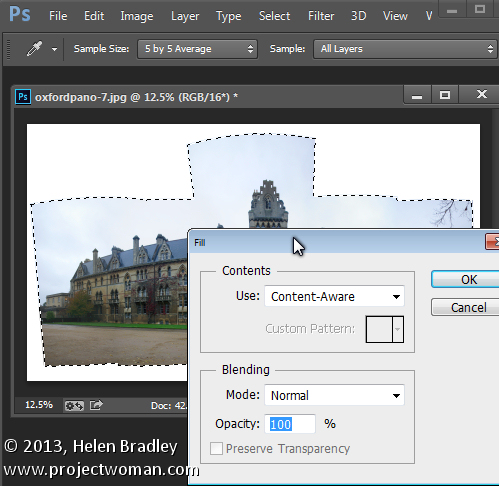
Select the area that you want to fill and then choose Edit > Fill, from the Use list choose Content Aware and click Ok. Photoshop will attempt to fill the missing area with details from the image around it. If the image contains sufficient detail you should be able to build up missing areas of sky and foreground, for example. If you encounter problems with the Content Aware Fill feature this post will show you how to mask a layer to get better results when using it: http://digital-photography-school.com/smarter-content-aware-fill-in-photoshop. Crop the image when you have filled the edge area.
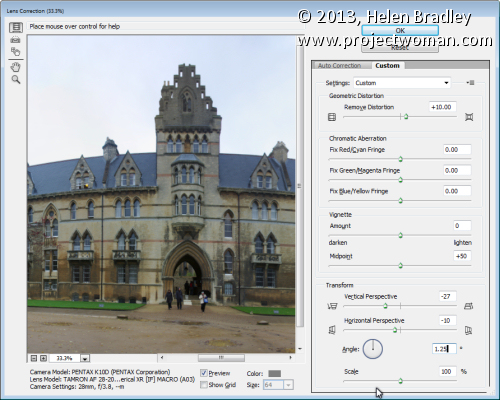
To fix unwanted distortion in an image you can use the Lens Correction tool. This tool works on a single layer and you run it by choosing Filter > Lens Correction > Manual. Adjust the Horizontal Perspective slider to fix problems with an image which has not been captured face onto the point of interest. Use the Vertical Perspective slider to adjust for keystoning – generally you will drag this slider to the left. Use the Geometric Distortion slider to remove barrel and pincushion distortion.
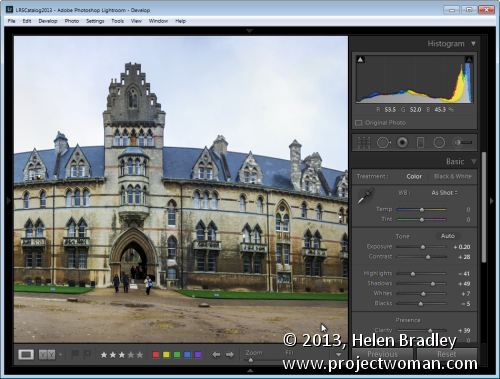
Once you have finished assembling the panorama choose File > Save to save the image and return to Lightroom where your panorama will be ready for further editing.
If you are not using Lightroom you can assemble a panorama from Bridge or from inside Photoshop. In Bridge select the panorama sequence and choose Tools > Photoshop > Photomerge in Bridge. In Photoshop, first open the images to use then choose File > Automate > Photomerge and click the Add Open Files button. In either case you will probably want to fix the image in Photoshop once the panorama is complete. If you are using Lightroom you may prefer to finish processing the panorama in Lightroom. Layout OptionsEach of the panorama Layout options in Photoshop results in a different looking panorama. Choosing Auto tells Photoshop to select the best of the options Perspective, Spherical and Cylindrical for your particular sequence of images. Here is the result of each of the other Layout options used with our image sequence, these results haven’t been edited except to straighten the image and brighten it a little. You may want to experiment with any given sequence of images to see which of these options gives you the most pleasing result: Perspective LayoutThe panorama is assembled in relation to the middle image of your sequence of images. The middle image is placed in position and the other images arranged either side of it and skewed and repositioned as needed. This often results in edges which are taller than the middle giving rise to the term ‘bow-tie” distortion.
Cylindrical LayoutThis layout avoids the bow-tie distortion by showing the images as they might look if placed on an unwrapped cylinder.
Spherical LayoutThis layout arranges the images as if to cover the inside of a sphere. It is a good choice for 360 degree panoramas and can also give good results with other shorter panorama sequences.
Collage LayoutThis layout aligns the images matching overlapping content. If necessary, image layers are transformed and rotated.
Reposition LayoutThis layout aligns the images matching overlapping content but without transforming or rotated the images.
Post originally from: Digital Photography Tips. Check out our more Photography Tips at Photography Tips for Beginners, Portrait Photography Tips and Wedding Photography Tips. Sending Panorama Sequences from Lightroom to Photoshop The post Sending Panorama Sequences from Lightroom to Photoshop by Helen Bradley appeared first on Digital Photography School. |
|
5 HOT Posts From Our Archives You Would Have Seen if You Were Following us on Facebook Posted: 06 Nov 2013 05:51 PM PST At dPS we have a little problem. As of this morning dPS has now published 4109 tutorials since we were founded back in 2006! That’s a lot of photographic learning hidden away in our archives and we’re increasingly aware that many of our readers have not seen some of our most helpful tips and tutorials. As a result – our team has been coming up with some strategies for highlighting some of the gold in our archives and have begun to experiment with some new ways of sharing it. How to See the Best Stuff in Our ArchivesThe most successful experiments so far have been centred around our Facebook page. Over the last few weeks we’e started sharing some of our best content from the past there to those who follow us – and the response has been amazing! In the past week alone we’ve had hundreds of thousands of people view, like, share and comment upon these links to old posts and have received a lot of positive feedback about sharing them. So if you want to explore our archives please Like Our Facebook page. If you do you’ll see us update around 4 times per day – the updates will be a combination of our new posts and old ones – as well as some fun challenges and discussions. To get a taste for what you’re missing – here’s the top 5 Facebook posts we’ve done this week:
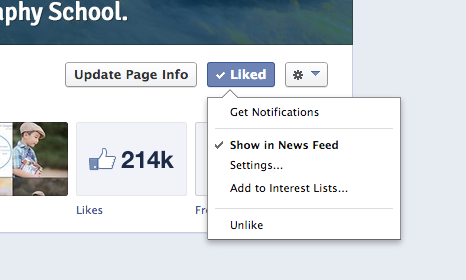
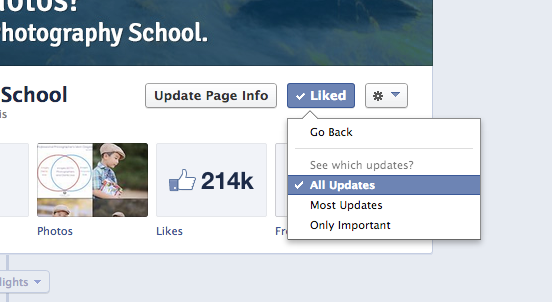
Also hot this week was a Facebook only challenge that we ran asking followers to submit a photo on the theme of CUTE. Following us on Facebook but Not Seeing Our Updates?Over the last few months Facebook have made changes that mean you don’t always see every post that people and pages you follow make. If you would like to see all our updates here’s what to do (this should take you 15 seconds at most): 1. Head to our Facebook Page 2. Make sure you’ve clicked our ‘like button’ (it should say ‘liked’ and have a tick next to it). 3. Once you’ve liked us – hover your cursor over the ‘liked’ button until a drop down menu appears (like the one pictured below).
4. Click the ‘settings’ option and you’ll see an option to choose ‘all updates’ (as you see below). If you select it you’re telling Facebook you want to see all of our updates.
5. You’re done – you should start seeing all our updates (that is if you check Facebook regularly). PS: we’ve also started featuring some of our new and old posts on our Google Plus page and plan to keep getting more active there too.
Post originally from: Digital Photography Tips. Check out our more Photography Tips at Photography Tips for Beginners, Portrait Photography Tips and Wedding Photography Tips. 5 HOT Posts From Our Archives You Would Have Seen if You Were Following us on Facebook The post 5 HOT Posts From Our Archives You Would Have Seen if You Were Following us on Facebook by Darren Rowse appeared first on Digital Photography School. |
|
Posted: 06 Nov 2013 10:59 AM PST
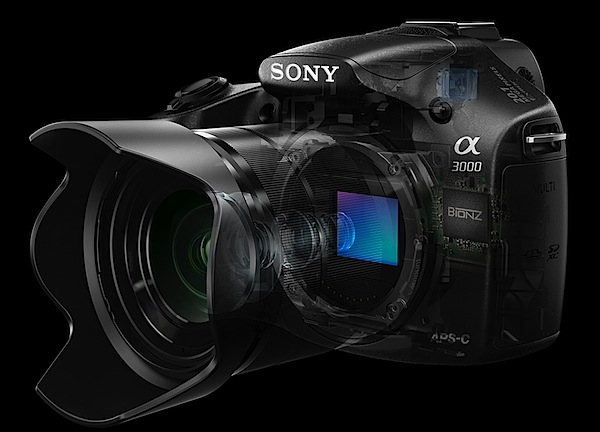
If you hanker for a DSLR and don’t have the budget for a high end full frame camera nor even enough $$$ for an APS-C sized sensor job, look this way… the news suddenly has suddenly got brighter. Most of the early action in mirrorless interchangeable lens cameras was in the area of models that offered viewing only via a rear screen, sometimes with an add on turret finder. But they just didn’t look like a DSLR!
Now Sony has come up with an appealing answer to a mirrorless interchangeable lens camera that has the appeal of a DSLR … with maybe a few less bells and whistles. The A3000 indeed has a traditional DSLR look and feel with a simple user interface. For one thing, you know you’re holding a DSLR with a traditional DSLR body shape and speed grip. To whet your appetite further, you can choose from 16 interchangeable E-mount lenses from Sony and Zeiss for a range of shooting options. The camera can shoot a maximum image size of 5456×3632 pixels, sufficient to make a 46x31cm print. [embedded content] Video can be shot in MPEG4 or AVCHD, with the latter offering Full HD 1920×1080 pixels. I was unable to shoot stills while recording video. HandlingThe camera is surprisingly small, easy to hold and well-balanced, at least it felt well-balanced with the f3.5-5.6/18-55mm OSS kit lens that was supplied with the review camera. Bear in mind that this is the package that is usually offered: body and 18-55mm lens. One Sony exec made the statement that ‘newcomers are often daunted by the complex settings found in traditional DSLR products … The 3000 user interface has been inspired by our easy to use NEX range of cameras.’ There are many key DSLR features in the camera, including a hot shoe and an eye level viewfinder. I ventured out in bright sun and at first found the viewfinder to be a dim alternative to the LCD screen, but then managed to successfully lift the brightness of both via a menu helper. To minimise total size and weight the A3000 accepts existing E-Mount lenses from the NEX family of products. Sony A3000 ControlsAt this point I have to disagree with the Sony spokesman. Firing up the camera with nary a glance at the instruction manual (thankfully available online) I found my early hours a mess of confusion. You can find the PDF of the full manual here. Confusion? For one thing there was no menu button, at least there was no button labelled ‘menu’. But let’s look it over.
Top deck: familiar territory, with the mode dial housing positions for intelligent and superior auto exposure, PASM, movie, sweep panorama and scene selection (presets for portrait, sports, macro, fireworks etc). Forward are the power and shutter buttons. At one corner is the replay button. Rear: just over the edge is the movie record button, which I feel could have been better placed at the camera’s far right corner. Then there are three unlabelled ‘soft keys’ — A, B and C — which take care of menu choices. Here’s how Sony describes the functions of these keys: ‘The soft keys have different roles, depending on the context. The assigned role (function) of each soft key is shown on the screen. To use the function shown at the upper right corner of the screen, press soft key A. To use the function shown at the lower right corner of the screen, press soft key B. To use the function shown at the center, press the center of the control wheel (soft key C). You can assign the functions to the soft key B.’ By careful inspection of the manual you can eventually suss out the functions of these three buttons but I found them to be a bit bewildering at first. Anyway … the control wheel has positions for burst shooting and the self timer, ISO setting, display options plus exposure correction and AF options.
Fifteen picture effects are accessible from the menu (soft key A). These include ‘artistic treatments’, like retro photo, miniature and partial colour. Sony’s sweep panorama feature is included that can shoot panos up to 12,416 x 1856 pixels in size. One note: unlike most interchangeable lens digicams, you need to manually blow away any dust on the sensor. Like this: ‘After turning off the camera, remove the lens and blow off dust on and around the image sensor surface using a blower.’ Careful! ISO TestsOnly at ISO 3200 was noise beginning to rise. At ISO 6400 noise up slightly but sharpness acceptable. At ISO 12800 noise up further, sharpness noticeably down and ugly artefacts evident. At ISO 16000 the show was over: noise up, sharpness down and ugly artefacts worse. Sony A3000 Review VerdictQuality: above average. Accurate colour. Why you’d buy the Sony A3000: small DSLR-like camera; access to lots of lenses. Why you wouldn’t buy the Sony A3000: menu access confusing. Sony A3000 Review Rating: 4 stars Sony A3000 SpecificationsImage Sensor: 20 million effective pixels.Metering: Multi segment, centre-weighted, spot.
Post originally from: Digital Photography Tips. Check out our more Photography Tips at Photography Tips for Beginners, Portrait Photography Tips and Wedding Photography Tips. The post Sony A3000 Review by Barrie Smith appeared first on Digital Photography School. |
|
The Path to Better Photography Posted: 06 Nov 2013 07:37 AM PST Ed Verosky is a professional photographer and author based in New York. In this article, Ed presents his recommended path to learning photography. This, along with his eBooks on the subject, have greatly improved the skills of thousands of photographers. To learn more about improving your photography, visit his site and check out his extensive eBook collection (currently 62% off at SnapnDeals). If you’ve ever wanted a little guidance when it comes to learning photography from top to bottom, this DPS post is for you! There’s a lot of information out there, and tons of books, tutorials, workshops, etc. to learn from. But it’s not always easy to know where to start, or where you should focus your efforts when it comes to really improving your knowledge of the art and craft of photography. With that in mind, here’s a “learning road map” I’ve put together for you that has helped many of my readers. I hope it helps you with your quest to become a better photographer.
Getting StartedFirst of all, I want to thank you for taking the time to read this. You’re probably looking at this right now, excited about the possibility that you might actually learn something new, something that will elevate you as a photographer in some way. Whether you are a beginning photographer, or someone who’s been at this for a few years, you probably have the desire to improve on this thing that you love. Photography means something special to you; it’s a kind of magic that allows you to express yourself. It’s your way of communicating and sharing with the world. Whether you’re doing what you love to earn extra income, or simply for the pure excitement and enjoyment of it, that’s reason enough to want to keep improving and learning and growing. It’s not only the technical skills, but the psychology and artistic sensibility of what we do as photographers that keeps us constantly in the need to learn and adapt to everything from new gear, to new people/clients, to our own ways of expressing ourselves. How to Use this Post as a GuidePrint this post out. It’s your guide and starting point. It can serve as a road map to learning the basics of photography, helping you to build a solid foundation from which to grow and become really good at what you do. I encourage you to use this road map and seek out multiple resources, like DPS, to further your understanding of each topic that follows. My blog, newsletter, video tutorials, and ebooks will also definitely help you learn about these things quickly and in great detail. But I routinely direct people to outside resources as well, because I think it’s important to learn from more than one teacher in order to really drive home the knowledge and principles of photography. I’m very excited about this journey you’re on, and it’s my goal to do everything in my power to help you get everything you want out of your photography. I’m obsessed with teaching and demonstrating what I’ve learned and all the new things I continue to learn. I’m sincerely happy that I have another person I can share this excitement with right now. That’s you! Now, we’ll begin our discussion of the four topics that I feel are most important in your development as a good photographer: the camera, the lighting, the subject, and post-processing. The CameraThe first part of becoming a complete photographer is knowing how your camera works, inside and out. Your camera is the main mode of communication between you and the outside world as a photographer. Like your voice, your photographic vocabulary is extremely limited without some good understanding of how best to tell a story. Put the effort into learning everything about your camera and and it will pay off, big time. Plus, you’ll be able to speak intelligently about your craft, and be able to ask the right questions when it comes to the topic of lighting. The camera and the lighting; knowledge of one topic supports an understanding of the other, so you need both. Start with your camera.
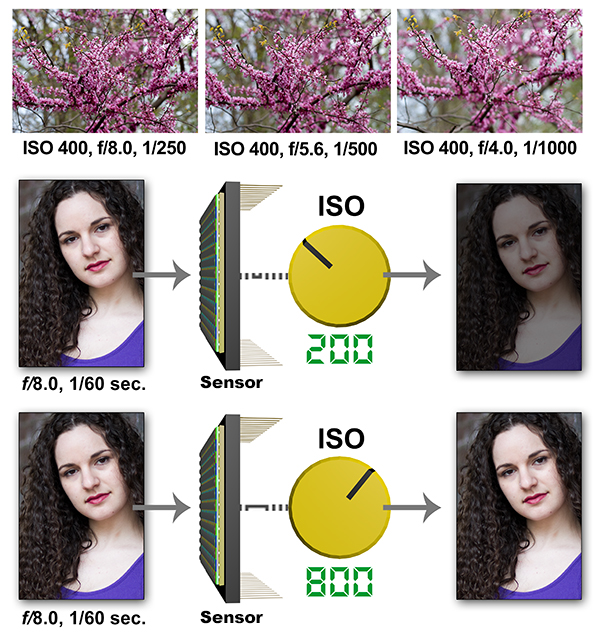
Good resources will provide numerous visual examples to help you understand how exposure works. The sequences above are just a few that I use in my eBooks to illustrate the interdependent nature of exposure controls on the camera. ———————– Here are some of the most important things you should learn about:
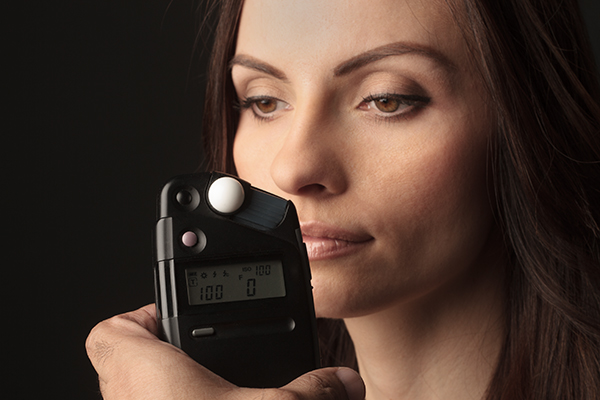
Ok, remember the broad list of things you need to learn: camera, lighting, subject, and post-processing? Well the list above is just the CAMERA part! Trust me, I know that part alone can seem overwhelming, and that’s why most people never bother to learn it all. That’s a real shame, because it’s the first part of becoming a complete photographer; you need to know everything about how your camera works. Fortunately, you don’t need to know everything from the start. If you’re using your camera in a way that’s working for you right now, keep doing that. There’s no reason to give that up. But in the meantime, start building on your current understanding and usage of the camera and learn a little bit more as the weeks go on. Soon, everything’s going to start coming together and you’ll find that you have a total command of the camera. That’s the goal. Read the best resources on using your DSLR, and just commit to wanting it. It’s going to happen, I promise! LightingAlthough setting your camera to one of the auto exposure modes is a great way to solve the immediate problem of getting a properly exposed image, it won’t solve your lighting concerns, and it’s your lighting that really makes the difference. Many photographers soon realize that what separates their images from better work is the application of good lighting techniques and different types of lighting sources. I would say that the ability to skillfully use lighting is the number one technical skill a photographer should seek to acquire in order to produce good work. Unfortunately, this is also the number one place photographers tend to drop the ball.
Learning how to control your light will allow you to easily create effects like overpowering daylight (above). Here, the right combination of camera settings and flash power create a nighttime effect, even though there is actually bright window light coming into the studio. ———————– Sure, lighting isn’t easy at first, and maybe that’s why so many photographers just give up on learning how to do it properly. It takes time, experimentation, and a good teacher to help you get to where you need to go with photographic lighting. Good books and tutorials can help you with that. When I teach, my goal is to show readers how to use natural, constant, and flash lighting in a way that really gives them a handle on it quickly. In order to really master lighting for photography, you should learn the following things:
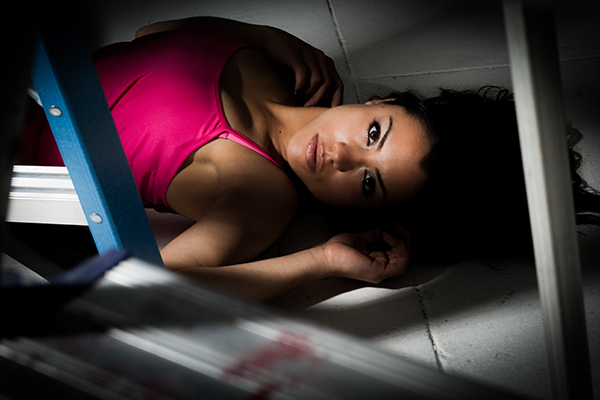
The SubjectI believe in teaching portraiture in a semi-traditional way; instructing on the fundamentals and quickly moving to a more freestyle approach. An appreciation for traditional lighting patterns and contemporary portraiture will give you a good foundation for all of your portraiture work. But in today’s marketplace, the old traditional portraiture isn’t the only game in town. Working photographers should look beyond typical portraiture to find ways to differentiate themselves from others. One of the main things I like to stress is that you should start thinking about unconventional posing, directing, lighting, etc. eventually developing your own style.
Great subjects can inspire you to get creative with your posing and lighting techniques. This type of experimentation will help you develop your own unique style. ———————– Again, this all begins with really knowing the fundamentals of lighting, and getting very comfortable with your gear so it becomes an extension of your vision and not something that gets in the way of the creative flow. But simply knowing how to use the tools and basic techniques of your craft isn’t enough. You need to let go of the things that hold you back from creating your best work and explore new ways to look at and create portraiture. Yes, the soft skills like working with subjects and clients are important which is why it’s one of my favorite things to teach. Here are some of the most important themes and topics I tend to discuss on a regular basis:
Post-ProcessingIt can be argued that post-processing happens the moment a digital camera processes the data off the sensor, and certainly when a file is converted, via some programmer’s algorithm, for view in a RAW conversion engine common in most digital workflows. Why not make the absolute most of the tools available to you, just as photographers have always done? It used to be darkroom tools, like various ways of developing film and selectively exposing photographic paper during the printing process, which allowed the photographer to enhance or correct problems with an original negative. Now it’s digital. Of course you can ruin any photograph with overdone effects or cheesy gimmicks. But used thoughtfully, post-processing techniques can help make a good picture an outstanding one.
Try out these products for free by clicking on the following links. You should see a “Trial” link on each product’s information page: Of course there are also other fun and effective ways to post-process your images, including using some popular mobile device apps. This is one of my favorite topics to cover as I’m a big fan of iPhone photography and mixing DSLR photography with phone photography editing and sharing technologies. Some of the things you might be interested in learning include:
This Is Just The StartI realize there’s a lot of information in this post. At the same time, it’s not complete, just one general outline based on my experience and teaching methods. But I strongly encourage you to find your place on this map and start navigating your way through it. It will take some time, but that’s one of the best things about photography, the discovery. —————— To get started, you can download my popular eBook bundle at a special discounted price (62% off) on SnapnDeals. Everything I’ve talked about above (and more) can be accessed now so you can get started today.
Post originally from: Digital Photography Tips. Check out our more Photography Tips at Photography Tips for Beginners, Portrait Photography Tips and Wedding Photography Tips. The Path to Better Photography The post The Path to Better Photography by Guest Contributor appeared first on Digital Photography School. |
| You are subscribed to email updates from Digital Photography School To stop receiving these emails, you may unsubscribe now. |
Email delivery powered by Google |
| Google Inc., 20 West Kinzie, Chicago IL USA 60610 | |